Causes of MPU (Metal Sticking):
- Uneven Pressure from the Caliper to the Pad: • The caliper applies uneven force to the brake pad. • This results in uneven pressure on the contact surface between the pad and the disc. • Leads to uneven wear, localized heat buildup, and increased risk of MPU.
- Issues with the Ceramic Composition of Friction Material: • Ceramic pads generally have low thermal conductivity and reduced graphite (lubricant) content. • Improper formulation leads to concentrated heat on the friction surface. • Causes rapid carbonization of the binder (phenolic resin), preventing the formation of a lubricating transfer film. • High temperature and pressure conditions form hard spots, increasing the likelihood of MPU.
- Entry of Solid Foreign Particles: • Hard contaminants may be introduced during production. • These particles cannot be removed during braking, causing MPU.
- Brake Disc Material Composition: • Elements such as carbon (C) and silicon (Si) oxidize when scraped onto the friction surface under high temperatures. • These solid oxides exacerbate MPU formation.
- Rust Accumulation: • Long-term parking may lead to heavy rusting of the brake disc. • Rust may be transferred to the brake pad or remain on the disc, leading to MPU and disc damage.
- High Ferrite Content in Brake Discs: • Excessive ferrite content reduces the hardness of the disc. • This increases the chances of MPU during braking.
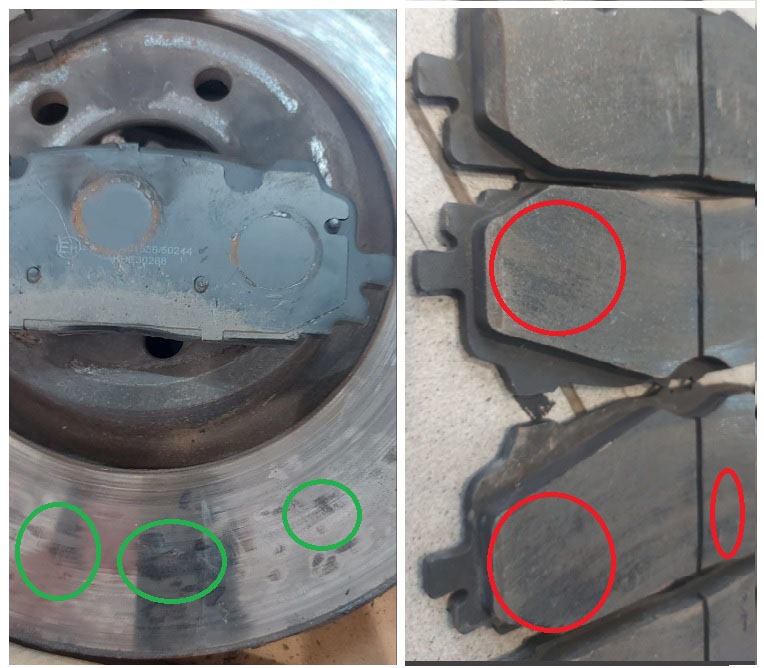
Recommended Measures: ✅ Inspect and diagnose the brake calipers for any faults. If any issues are found, repair or replace them based on the severity and nature of the damage.
